Communication in Turtles and Why It Matters
Discover how turtles communicate through body language, sounds, and scents. Learn to understand your pet turtle's signals for better bonding and care.

Turtles, often perceived as quiet creatures, actually have their own unique ways of communicating. Understanding these methods is not just a matter of pet care, but a key to deepening your bond with your pet.
This guide will delve into the different ways turtles express themselves, from body language to sounds and scents. By mastering the art of turtle communication, you can better meet your pet's needs and foster a stronger connection.

Mechanisms and Significance of Communication in Turtles
Turtles, though commonly perceived as quiet and solitary, employ various communicative behaviors that facilitate social interaction, resource competition, and reproductive processes. While turtle communication is not as overtly vocal as many other reptiles, certain species produce low-frequency sounds or hissing in response to stress or mating contexts. Visual cues, including head bobbing, limb movements, and specific shell displays, are also used to convey aggression, courtship interest, or territorial warnings. In semi-aquatic and aquatic turtles, tactile communication—often involving biting or nudging—can signal dominance or reproductive readiness.
Environmental factors significantly shape communicative mechanisms. For instance, water transmits vibrations and chemical cues effectively, which may partly explain the prevalence of body language and chemoreception in turtles. Some research suggests that females detect subtle chemical signals from males, influencing mate selection and courtship behaviors. Additionally, the ability to store sperm for extended periods indicates a reproductive strategy less dependent on constant communication or courtship events, as long as initial mating interactions are successful.
Communication in turtles is thus a multifaceted phenomenon, integrating vocal, visual, chemical, and tactile elements tailored to specific ecological niches. These behaviors not only ensure successful mating and offspring survival but also maintain social structures and individual well-being within turtle populations.
Sources
– Gibbons, J.W. Turtles of the Southeast.
– Mittermeier, R.A. & Vetter, H. Turtles of the World.
– Vogt, R.C. Natural History of Turtles, Snakes, Frogs, and Salamanders.
Body Language
Turtles communicate in subtle yet telling ways through their body positions and movements. Observing head bobbing, neck stretching, and shell posture can help you decode whether they’re feeling curious, anxious, or confident.
For instance, a turtle bobbing its head might be showing dominance or interest, while one tucking limbs and head in signals caution or fear. A raised shell can indicate an attempt to look bigger and more intimidating, whereas a flattened shell often shows calmness or submission. Learning these cues encourages stronger bonds and better care for your turtle.
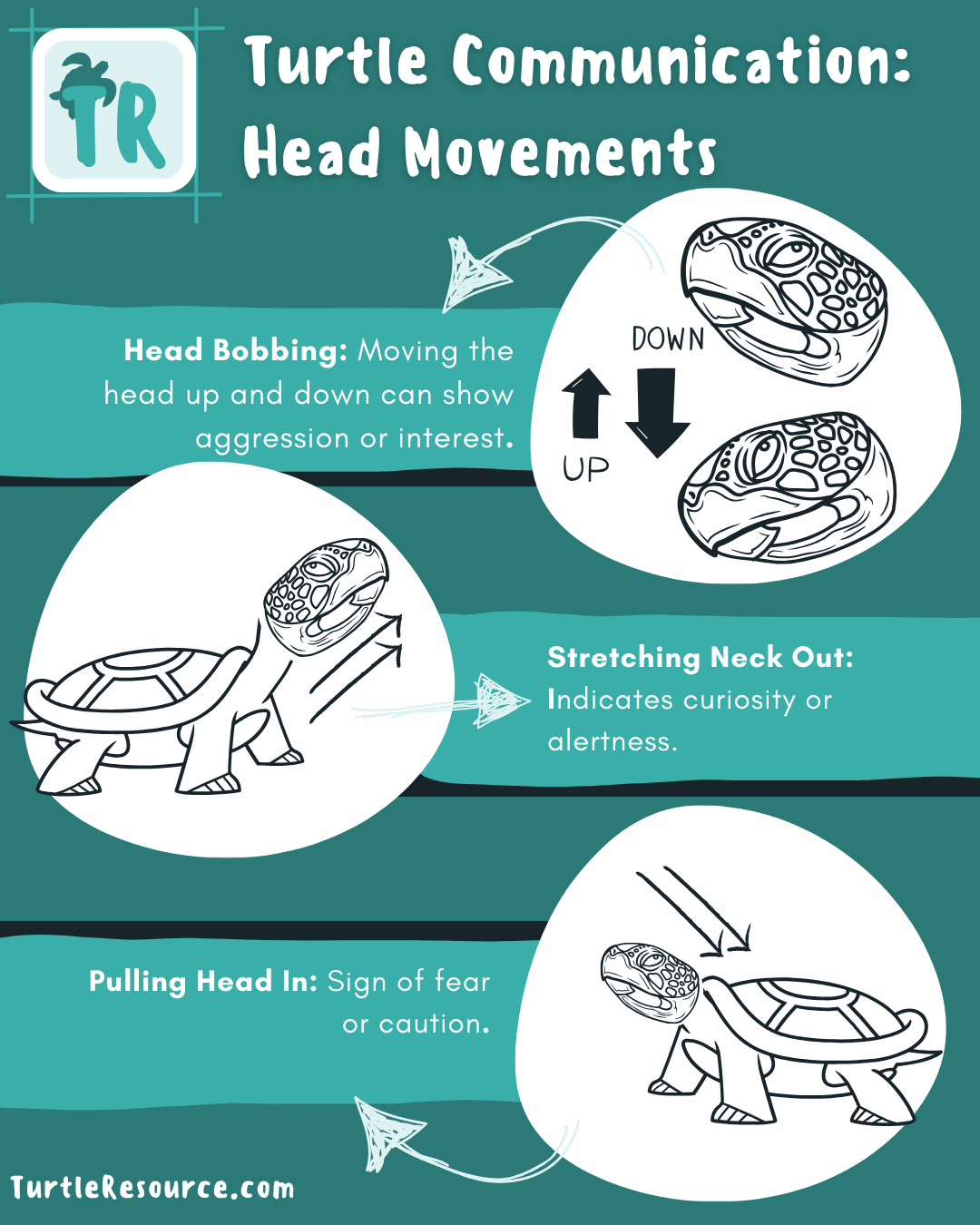
Head Movements
- Head Bobbing: Moving the head up and down can show aggression or interest.
- Stretching Neck Out: Indicates curiosity or alertness.
- Pulling Head In: Sign of fear or caution.
Limb Positions
- Extended Limbs: Relaxed and comfortable.
- Tucked Limbs: Feeling threatened or shy.
Shell Posture
- Raised Shell: Trying to appear more prominent when threatened.
- Flattened Shell: Submissive or relaxed state.
Vocalizations
Turtles aren’t known for loud calls, but they do make unique sounds to share how they feel. Hissing often signals alarm or a need for personal space, warning others to keep their distance.
Grunts and sighs can surface during strenuous activities like digging or mating, hinting at effort or slight discomfort. Meanwhile, chirping—mostly heard from hatchlings—may mean they’re seeking care or expressing a need.
Understanding these faint vocalizations helps turtle keepers and enthusiasts alike detect stress, needs, and mood, fostering a healthier and more attentive environment for these fascinating reptiles.
Hissing
- Cause: Often a defensive reaction when startled.
- Meaning: "Stay away" or "I'm scared."
Grunting and Sighing
- Cause: This may occur during physical activity like digging or mating.
- Meaning: Effort or discomfort.
Chirping
- Cause: Some baby turtles make chirping noises.
- Meaning: Seeking attention or expressing needs.
Scent Communication
Turtles often rely on scent to share messages. They produce pheromones through specialized glands, helping attract mates or mark territory. By rubbing their bodies on objects, they leave a signature smell that other turtles can detect and interpret.
Pheromones
- Purpose: Attracting mates or marking territory.
- Release: Glands produce scents that other turtles can detect.
Scent Marking
- Behavior: Rubbing their body on objects to leave a scent.
- Meaning: Claiming an area or signaling readiness to mate.
Visual Displays
Colors and patterns are powerful signals among turtles. Males may show brighter colors to draw attention during mating season, while dull colors can point to stress or illness. Shell markings serve like IDs, aiding in recognition, and a shell’s size or shape can indicate age or maturity.
Take note that not all turtles change colors. This is a very situational scenario but highly likely when the environment is right.

Color Changes
- Brighter Colors: Often seen in males during mating season to attract females.
- Dull Colors: May indicate stress or illness.
Learn more about turtle health to keep your pet well and active.
Shell Patterns
- Unique Markings: Help turtles recognize each other.
- Size and Shape: Can signal age and maturity.
Touch and Interaction
Physical contact speaks volumes in turtle communication. Playful nips might be curiosity or bonding, but aggressive bites warn of territory defense or discomfort. Gentle nudging can request attention or food, and persistent pushes may reveal impatience or urgency.
Biting and Nipping
- Playful Nips: This can be a way to explore or interact.
- Aggressive Bites: Sign of territory defense or discomfort.
Nudging
- Gentle Pushes: May signal a desire for attention or food.
- Persistent Nudging: This could indicate impatience or urgency.
Tame Your Turtle to Reduce Bites
Credits: Carson’s Aquatics
Understanding Your Turtle
Observing your turtle's behaviors lets you learn what they are trying to tell you. Turtle communication isn't only about learning how these reptiles communicate but also about being aware of your pet's behavior.
Recognizing Emotions
- Relaxed Turtle: Basking with limbs stretched out.
- Stressed Turtle: Hiding frequently or showing aggression.
Responding Appropriately
- Give Space: Provide a quiet environment if your turtle pulls back or hisses.
- Interact Gently: Approach slowly and handle with care.
Enhancing Turtle Communication
Strengthen your bond with your turtle through attentive care. This can include providing a comfortable habitat, regular feeding and interaction, and even introducing new toys or objects for exploration to keep your turtle engaged and happy.
Routine
- Consistent Feeding Times: Helps your turtle feel secure.
- Regular Interaction: Builds trust over time.
Environment
- Comfortable Habitat: Meets physical and emotional needs.
- Enrichment: Provide toys or objects for exploration.
Conclusion
Turtles communicate in subtle but meaningful ways. By paying attention to their body language, sounds, and behaviors, you can better understand your pet's needs and feelings. This understanding leads to a stronger relationship and a happier, healthier turtle.
Take the time to observe and interact with your turtle, and you'll discover the unique ways they express themselves. This active engagement not only enriches your pet's life but also deepens your connection with them.
